Kubernetes быстро стал стандартом для доставки, масштабирования и управления контейнерными приложениями.
Это очень гибкое и универсальное решение с открытым исходным кодом.
Имеет обширную документацию, и не всегда легко найти нужный раздел.
Вот почему Kubernetes так сложно освоить.
После планирования кластера его еще нужно установить, и здесь тоже не все гладко.
Вот почему существуют такие инструменты развертывания, как Кубеспрей, которые облегчат вашу работу.
Я расскажу об автоматическом развертывании кластера Kubernetes с помощью Kubespray в облаке OpenStack (Open Telekom Cloud).
Для автоматического развертывания Kubernetes Kubespray использует инструмент подготовки, настройки и доставки приложений Ansible. Kubespray также предоставляет библиотеку для инициализации ресурсов на разных облачных платформах.
Это делается с помощью инструмента Terraform «инфраструктура как код».
Теперь проект Kubespray поддерживает Терраформ для AWS, OpenStack и пакетных облаков.
Этот инструмент используется совместно с библиотека OpenStack, для обеспечения инфраструктуры в этом сценарии.
Требования
Сначала давайте рассмотрим предварительные условия для развертывания.Они разделены на две категории: требования Kubespray и требования к библиотекам поставщиков.
Kubespray требует следующих компонентов:
- Python 2.7 (или выше)
- Ansible 2.7 (или выше)
- Джинджа 2.9 (или выше)
- Терраформ 0.11 (или выше)
Затем путь к распакованному файлу необходимо сохранить в переменной PATH. Вы можете использовать команду terraform, чтобы проверить, все ли установлено.
Вы можете узнать больше Здесь.
В зависимости от операционной системы Ansible можно установить с помощью пары команд. См.
Здесь я использую Ubuntu и устанавливаю Ansible следующим образом.
Далее вам необходимо установить зависимости Kubespray. Это делается с помощью следующей команды.sudo apt update sudo apt install ansible
Но сначала вам нужно клонировать репозиторий.
git clone https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/kubespray
sudo pip install -r requirements.txt
Чтобы использовать Open Telekom Cloud, настройте данные доступа с помощью .
ostackrc в корневом каталоге и загрузите переменные среды.
Кластерное планирование
Kubernetes очень гибок, поэтому кластер можно адаптировать под ваши нужды.Здесь мы не будем рассматривать разные варианты кластеров.
Об этом можно прочитать в документации Kubernetes в разделе Создание собственного кластера с нуля.
Например, мы создадим кластер из мастера с etcd и двух рабочих нод. У кластера не будет плавающего IP-адреса, поэтому он не будет доступен из Интернета.
Нам также нужно выбрать CNI (сетевой интерфейс контейнера).
Есть несколько вариантов (ресничка, бязь, фланель, плетение сеткой и т. д.), но мы возьмем фланель, которую не нужно настраивать.
Ситец тоже подойдет, но вам понадобится настроить порты OpenStack Neutron для сервисных подсетей и модулей.
Чтобы управлять кластерами на панели управления Kubernetes после развертывания, нам необходимо установить панель управления.
Настройка конфигурации кластера
Выполните следующие команды в каталоге репозитория, указав желаемое имя в переменной $CLUSTER. cp -LRp contrib/terraform/openstack/sample-inventory \
inventory/$CLUSTER
cd inventory/$CLUSTER
ln -s .
/.
/contrib/terraform/openstack/hosts
ln -s .
/.
/contrib
После выполнения команд отредактируйте файл Inventory/$CLUSTER/cluster.tf.
# your Kubernetes cluster name here
cluster_name = "k8s-test-cluster"
az_list=["eu-de-01", "eu-de-02"]
dns_nameservers=["100.125.4.25", "8.8.8.8"]
# SSH key to use for access to nodes
public_key_path = "~/.
ssh/id_rsa.pub"
# image to use for bastion, masters, standalone etcd instances, and nodes
image = "Standard_CentOS_7_latest"
# user on the node (ex. core on Container Linux, ubuntu on Ubuntu, etc.)
ssh_user = "linux"
# 0|1 bastion nodes
number_of_bastions = 0
flavor_bastion = "s2.xlarge.4"
# standalone etcds
number_of_etcd = 0
flavor_etcd = "s2.xlarge.4"
# masters
number_of_k8s_masters = 0
number_of_k8s_masters_no_etcd = 0
number_of_k8s_masters_no_floating_ip = 1
number_of_k8s_masters_no_floating_ip_no_etcd = 0
flavor_k8s_master = "s2.xlarge.4"
# nodes
number_of_k8s_nodes = 0
number_of_k8s_nodes_no_floating_ip = 2
flavor_k8s_node = "s2.xlarge.4"
# GlusterFS
# either 0 or more than one
#number_of_gfs_nodes_no_floating_ip = 1
#gfs_volume_size_in_gb = 150
# Container Linux does not support GlusterFS
image_gfs = "Standard_CentOS_7_latest"
# May be different from other nodes
#ssh_user_gfs = "linux"
#flavor_gfs_node = "s2.xlarge.4"
# networking
network_name = "k8s-test-network"
external_net = "Externel_Network_ID"
subnet_cidr = "192.168.100.0/24"
floatingip_pool = "admin_external_net"
bastion_allowed_remote_ips = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
Прочтите описание переменных Здесь.
В этом примере мы создадим кластер с одним главным и двумя рабочими узлами Kubernetes на основе последней версии CentOS 7 и s2.xlarge.4. Мы также установим etcd на мастер-сервер.
Развертывание инфраструктуры
Теперь мы готовы развернуть кластерную инфраструктуру с помощью Terraform. На рисунке показано, как выглядит инфраструктура после развертывания.Подробности ниже.
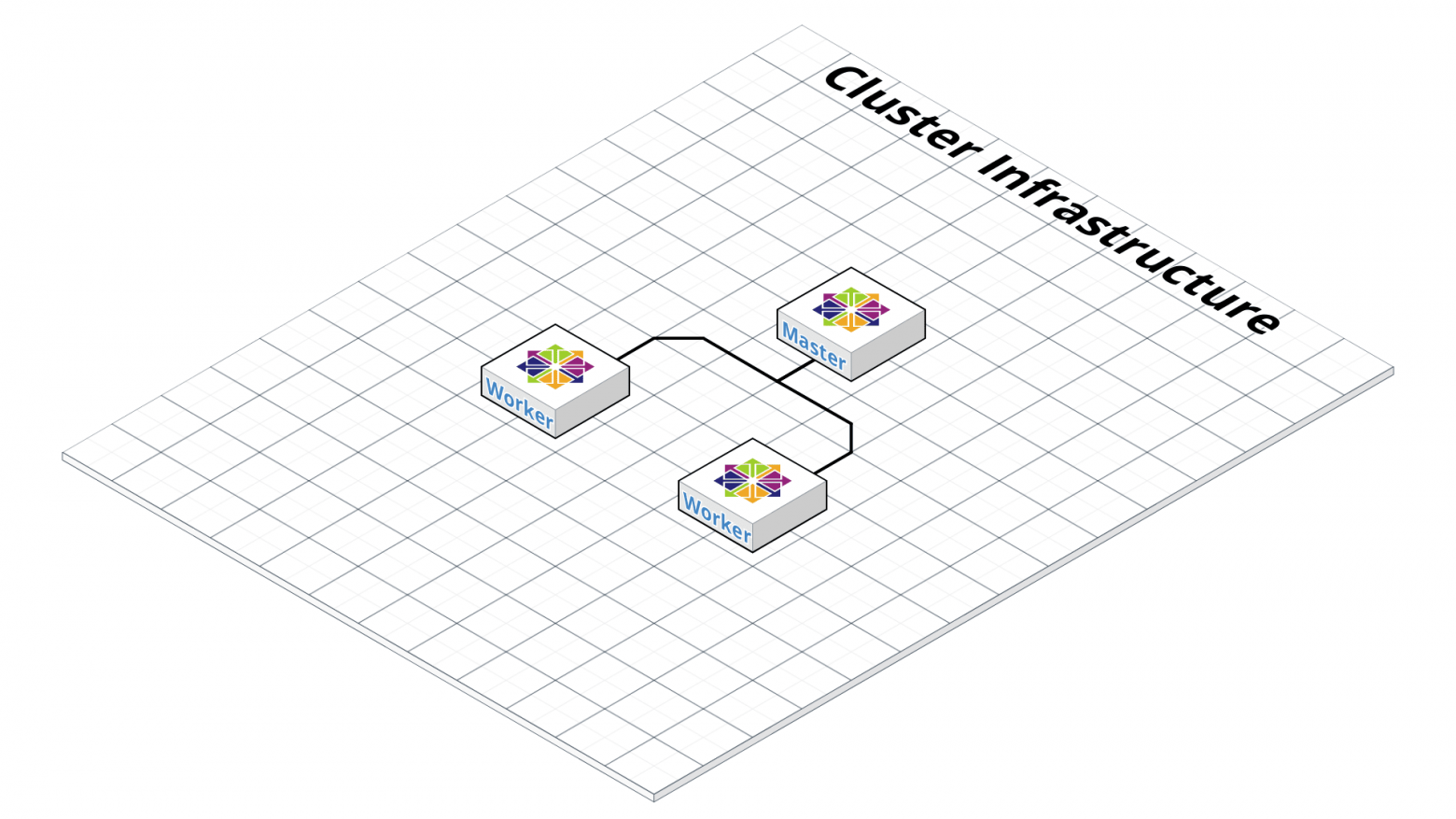
Чтобы начать развертывание Terraform, перейдите в каталог Inventory/$CLUSTER/ и выполните следующие команды.
Для начала давайте установим необходимые плагины.
Для этого нам понадобится аргумент init и путь к плагинам.
terraform init .
/.
/contrib/terraform/openstack
Эта операция выполняется очень быстро.
Теперь Terraform готов к развертыванию инфраструктуры с помощью аргумента Apply. terraform apply -var-file=cluster.tf .
/.
/contrib/terraform/openstack
Через несколько секунд Terraform должен показать аналогичный результат, и экземпляры станут доступны для использования.
Apply complete! Resources: 3 added, 0 changed, 0 destroyed.
Чтобы проверить доступность серверов, выполните следующую команду Ansible, после чего перейдем в корневую папку репозитория.
$ ansible -i inventory/$CLUSTER/hosts -m ping all
example-k8s_node-1 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
example-etcd-1 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
example-k8s-master-1 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
Развертывание кластера Kubernetes
Инфраструктура развернута, теперь нужно установить кластер Kubernetes. Сначала давайте настроим переменные кластера в файле Inventory/$CLUSTER/group_vars/all/all.yml. Здесь вам нужно установить для cloud_provider значение openstack, а для bin_dir — путь, куда будут установлены файлы.В нашем примере мы используем следующую конфигурацию.
## Directory where etcd data stored
etcd_data_dir: /var/lib/etcd
## Directory where the binaries will be installed
bin_dir: /usr/local/bin
## The access_ip variable is used to define how other nodes should access
## the node. This is used in flannel to allow other flannel nodes to see
## this node for example. The access_ip is really useful AWS and Google
## environments where the nodes are accessed remotely by the "public" ip,
## but don't know about that address themselves.
#access_ip: 1.1.1.1
## External LB example config
## apiserver_loadbalancer_domain_name: "elb.some.domain"
#loadbalancer_apiserver:
# address: 1.2.3.4
# port: 1234
## Internal loadbalancers for apiservers
#loadbalancer_apiserver_localhost: true
## Local loadbalancer should use this port instead, if defined.
## Defaults to kube_apiserver_port (6443)
#nginx_kube_apiserver_port: 8443
### OTHER OPTIONAL VARIABLES
## For some things, kubelet needs to load kernel modules. For example, dynamic kernel services are needed
## for mounting persistent volumes into containers. These may not be loaded by preinstall kubernetes
## processes. For example, ceph and rbd backed volumes. Set to true to allow kubelet to load kernel
## modules.
#kubelet_load_modules: false
## Upstream dns servers used by dnsmasq
#upstream_dns_servers:
# - 8.8.8.8
# - 8.8.4.4
## There are some changes specific to the cloud providers
## for instance we need to encapsulate packets with some network plugins
## If set the possible values are either 'gce', 'aws', 'azure', 'openstack', 'vsphere', 'oci', or 'external'
## When openstack is used make sure to source in the openstack credentials
## like you would do when using nova-client before starting the playbook.
## Note: The 'external' cloud provider is not supported.
## TODO(riverzhang): https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/administer-cluster/running-cloud-controller/#running-cloud-controller-manager
cloud_provider: openstack
## Set these proxy values in order to update package manager and docker daemon to use proxies
#http_proxy: ""
#https_proxy: ""
## Refer to roles/kubespray-defaults/defaults/main.yml before modifying no_proxy
#no_proxy: ""
## Some problems may occur when downloading files over https proxy due to ansible bug
## https://github.com/ansible/ansible/issues/32750 .
Set this variable to False to disable
## SSL validation of get_url module. Note that kubespray will still be performing checksum validation.
#download_validate_certs: False
## If you need exclude all cluster nodes from proxy and other resources, add other resources here.
#additional_no_proxy: ""
## Certificate Management
## This setting determines whether certs are generated via scripts.
## Chose 'none' if you provide your own certificates.
## Option is "script", "none"
## note: vault is removed
#cert_management: script
## Set to true to allow pre-checks to fail and continue deployment
#ignore_assert_errors: false
## The read-only port for the Kubelet to serve on with no authentication/authorization. Uncomment to enable.
#kube_read_only_port: 10255
## Set true to download and cache container
download_container: false
## Deploy container engine
# Set false if you want to deploy container engine manually.
#deploy_container_engine: true
## Set Pypi repo and cert accordingly
#pyrepo_index: https://pypi.example.com/simple
#pyrepo_cert: /etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt
Теперь давайте настроим файл Inventory/$CLUSTER/group_vars/k8s-cluster/k8s-cluster.yml. Задайте для переменной kube_network_plugin значение фланель или бязь (необходимо настройка портов OpenStack Neutron ).
Для нас это будет фланель, которую не нужно настраивать.
Для переменной resolvconf_mode установите docker_dns. Это значение указывает Kubespray на необходимость установки Параметры демона Docker. Ниже вы можете увидеть пример конфигурации нашего кластера.
# Kubernetes configuration dirs and system namespace.
# Those are where all the additional config stuff goes
# the kubernetes normally puts in /srv/kubernetes.
# This puts them in a sane location and namespace.
# Editing those values will almost surely break something.
kube_config_dir: /etc/kubernetes
kube_script_dir: "{{ bin_dir }}/kubernetes-scripts"
kube_manifest_dir: "{{ kube_config_dir }}/manifests"
# This is where all the cert scripts and certs will be located
kube_cert_dir: "{{ kube_config_dir }}/ssl"
# This is where all of the bearer tokens will be stored
kube_token_dir: "{{ kube_config_dir }}/tokens"
# This is where to save basic auth file
kube_users_dir: "{{ kube_config_dir }}/users"
kube_api_anonymous_auth: true
## Change this to use another Kubernetes version, e.g. a current beta release
kube_version: v1.13.3
# kubernetes image repo define
kube_image_repo: " gcr.io/google-containers "
# Where the binaries will be downloaded.
# Note: ensure that you've enough disk space (about 1G)
local_release_dir: "/tmp/releases"
# Random shifts for retrying failed ops like pushing/downloading
retry_stagger: 5
# This is the group that the cert creation scripts chgrp the
# cert files to. Not really changeable.
kube_cert_group: kube-cert
# Cluster Loglevel configuration
kube_log_level: 2
# Directory where credentials will be stored
credentials_dir: "{{ inventory_dir }}/credentials"
# Users to create for basic auth in Kubernetes API via HTTP
# Optionally add groups for user
kube_api_pwd: "{{ lookup('password', credentials_dir + '/kube_user.creds length=15 chars=ascii_letters,digits') }}"
kube_users:
kube:
pass: "{{kube_api_pwd}}"
role: admin
groups:
- system:masters
## It is possible to activate / deactivate selected authentication methods (basic auth, static token auth)
#kube_oidc_auth: false
#kube_basic_auth: false
#kube_token_auth: false
## Variables for OpenID Connect Configuration https://kubernetes.io/docs/admin/authentication/
## To use OpenID you have to deploy additional an OpenID Provider (e.g Dex, Keycloak, .
) # kube_oidc_url: https:// .
# kube_oidc_client_id: kubernetes ## Optional settings for OIDC # kube_oidc_ca_file: "{{ kube_cert_dir }}/ca.pem" # kube_oidc_username_claim: sub # kube_oidc_username_prefix: oidc: # kube_oidc_groups_claim: groups # kube_oidc_groups_prefix: oidc: # Choose network plugin (cilium, calico, contiv, weave or flannel) # Can also be set to 'cloud', which lets the cloud provider setup appropriate routing kube_network_plugin: flannel # Setting multi_networking to true will install Multus: https://github.com/intel/multus-cni kube_network_plugin_multus: false # Kubernetes internal network for services, unused block of space. kube_service_addresses: 10.233.0.0/18 # internal network. When used, it will assign IP # addresses from this range to individual pods. # This network must be unused in your network infrastructure! kube_pods_subnet: 10.233.64.0/18 # internal network node size allocation (optional).
This is the size allocated # to each node on your network. With these defaults you should have # room for 4096 nodes with 254 pods per node. kube_network_node_prefix: 24 # The port the API Server will be listening on. kube_apiserver_ip: "{{ kube_service_addresses|ipaddr('net')|ipaddr(1)|ipaddr('address') }}" kube_apiserver_port: 6443 # (https) #kube_apiserver_insecure_port: 8080 # (http) # Set to 0 to disable insecure port - Requires RBAC in authorization_modes and kube_api_anonymous_auth: true kube_apiserver_insecure_port: 0 # (disabled) # Kube-proxy proxyMode configuration. # Can be ipvs, iptables kube_proxy_mode: ipvs # A string slice of values which specify the addresses to use for NodePorts. # Values may be valid IP blocks (e.g. 1.2.3.0/24, 1.2.3.4/32).
# The default empty string slice ([]) means to use all local addresses. # kube_proxy_nodeport_addresses_cidr is retained for legacy config kube_proxy_nodeport_addresses: >- {%- if kube_proxy_nodeport_addresses_cidr is defined -%} [{{ kube_proxy_nodeport_addresses_cidr }}] {%- else -%} [] {%- endif -%} # If non-empty, will use this string as identification instead of the actual hostname #kube_override_hostname: >- # {%- if cloud_provider is defined and cloud_provider in [ 'aws' ] -%} # {%- else -%} # {{ inventory_hostname }} # {%- endif -%} ## Encrypting Secret Data at Rest (experimental) kube_encrypt_secret_data: false # DNS configuration. # Kubernetes cluster name, also will be used as DNS domain cluster_name: cluster.local # Subdomains of DNS domain to be resolved via /etc/resolv.conf for hostnet pods ndots: 2 # Can be dnsmasq_kubedns, kubedns, coredns, coredns_dual, manual or none dns_mode: coredns # Set manual server if using a custom cluster DNS server #manual_dns_server: 10.x.x.x # Enable nodelocal dns cache enable_nodelocaldns: False nodelocaldns_ip: 169.254.25.10 # Can be docker_dns, host_resolvconf or none resolvconf_mode: docker_dns # Deploy netchecker app to verify DNS resolve as an HTTP service deploy_netchecker: false # Ip address of the kubernetes skydns service skydns_server: "{{ kube_service_addresses|ipaddr('net')|ipaddr(3)|ipaddr('address') }}" skydns_server_secondary: "{{ kube_service_addresses|ipaddr('net')|ipaddr(4)|ipaddr('address') }}" dnsmasq_dns_server: "{{ kube_service_addresses|ipaddr('net')|ipaddr(2)|ipaddr('address') }}" dns_domain: "{{ cluster_name }}" ## Container runtime ## docker for docker and crio for cri-o. container_manager: docker ## Settings for containerized control plane (etcd/kubelet/secrets) etcd_deployment_type: docker kubelet_deployment_type: host helm_deployment_type: host # K8s image pull policy (imagePullPolicy) k8s_image_pull_policy: IfNotPresent # audit log for kubernetes kubernetes_audit: false # dynamic kubelet configuration dynamic_kubelet_configuration: false # define kubelet config dir for dynamic kubelet #kubelet_config_dir: default_kubelet_config_dir: "{{ kube_config_dir }}/dynamic_kubelet_dir" dynamic_kubelet_configuration_dir: "{{ kubelet_config_dir | default(default_kubelet_config_dir) }}" # pod security policy (RBAC must be enabled either by having 'RBAC' in authorization_modes or kubeadm enabled) podsecuritypolicy_enabled: false # Make a copy of kubeconfig on the host that runs Ansible in {{ inventory_dir }}/artifacts # kubeconfig_localhost: false # Download kubectl onto the host that runs Ansible in {{ bin_dir }} # kubectl_localhost: false # dnsmasq # dnsmasq_upstream_dns_servers: # - / resolvethiszone.with/10.0.4.250 # - 8.8.8.8 # Enable creation of QoS cgroup hierarchy, if true top level QoS and pod cgroups are created. (default true) # kubelet_cgroups_per_qos: true # A comma separated list of levels of node allocatable enforcement to be enforced by kubelet. # Acceptable options are 'pods', 'system-reserved', 'kube-reserved' and ''.
Default is "".
# kubelet_enforce_node_allocatable: pods
## Supplementary addresses that can be added in kubernetes ssl keys.
## That can be useful for example to setup a keepalived virtual IP
# supplementary_addresses_in_ssl_keys: [10.0.0.1, 10.0.0.2, 10.0.0.3]
## Running on top of openstack vms with cinder enabled may lead to unschedulable pods due to NoVolumeZoneConflict restriction in kube-scheduler.
## See https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/kubespray/issues/2141
## Set this variable to true to get rid of this issue
volume_cross_zone_attachment: false
# Add Persistent Volumes Storage Class for corresponding cloud provider ( OpenStack is only supported now )
persistent_volumes_enabled: false
## Container Engine Acceleration
## Enable container acceleration feature, for example use gpu acceleration in containers
# nvidia_accelerator_enabled: true
## Nvidia GPU driver install. Install will by done by a (init) pod running as a daemonset.
## Important: if you use Ubuntu then you should set in all.yml 'docker_storage_options: -s overlay2'
## Array with nvida_gpu_nodes, leave empty or comment if you dont't want to install drivers.
## Labels and taints won't be set to nodes if they are not in the array.
# nvidia_gpu_nodes:
# - kube-gpu-001
# nvidia_driver_version: "384.111"
## flavor can be tesla or gtx
# nvidia_gpu_flavor: gtx
Наконец, давайте отредактируем файл Inventory/$CLUSTER/group_vars/k8s-cluster/addons.yml и установим для Dashboard_enabled значение true, чтобы установить панель мониторинга.
Пример конфигурации: # Kubernetes dashboard
# RBAC required. see docs/getting-started.md for access details.
dashboard_enabled: true
# Helm deployment
helm_enabled: false
# Registry deployment
registry_enabled: false
# registry_namespace: kube-system
# registry_storage_class: ""
# registry_disk_size: "10Gi"
# Metrics Server deployment
metrics_server_enabled: false
# metrics_server_kubelet_insecure_tls: true
# metrics_server_metric_resolution: 60s
# metrics_server_kubelet_preferred_address_types: "InternalIP"
# Local volume provisioner deployment
local_volume_provisioner_enabled: false
# local_volume_provisioner_namespace: kube-system
# local_volume_provisioner_storage_classes:
# local-storage:
# host_dir: /mnt/disks
# mount_dir: /mnt/disks
# fast-disks:
# host_dir: /mnt/fast-disks
# mount_dir: /mnt/fast-disks
# block_cleaner_command:
# - "/scripts/shred.sh"
# - "2"
# volume_mode: Filesystem
# fs_type: ext4
# CephFS provisioner deployment
cephfs_provisioner_enabled: false
# cephfs_provisioner_namespace: "cephfs-provisioner"
# cephfs_provisioner_cluster: ceph
# cephfs_provisioner_monitors: "172.24.0.1:6789,172.24.0.2:6789,172.24.0.3:6789"
# cephfs_provisioner_admin_id: admin
# cephfs_provisioner_secret: secret
# cephfs_provisioner_storage_class: cephfs
# cephfs_provisioner_reclaim_policy: Delete
# cephfs_provisioner_claim_root: /volumes
# cephfs_provisioner_deterministic_names: true
# Nginx ingress controller deployment
ingress_nginx_enabled: false
# ingress_nginx_host_network: false
# ingress_nginx_nodeselector:
# node.kubernetes.io/node: ""
# ingress_nginx_tolerations:
# - key: "node.kubernetes.io/master"
# operator: "Equal"
# value: ""
# effect: "NoSchedule"
# ingress_nginx_namespace: "ingress-nginx"
# ingress_nginx_insecure_port: 80
# ingress_nginx_secure_port: 443
# ingress_nginx_configmap:
# map-hash-bucket-size: "128"
# ssl-protocols: "SSLv2"
# ingress_nginx_configmap_tcp_services:
# 9000: "default/example-go:8080"
# ingress_nginx_configmap_udp_services:
# 53: "kube-system/kube-dns:53"
# Cert manager deployment
cert_manager_enabled: false
# cert_manager_namespace: "cert-manager"
Изменив конфигурацию, давайте запустим ansible-playbook с нашей конфигурацией, выполнив следующую команду.
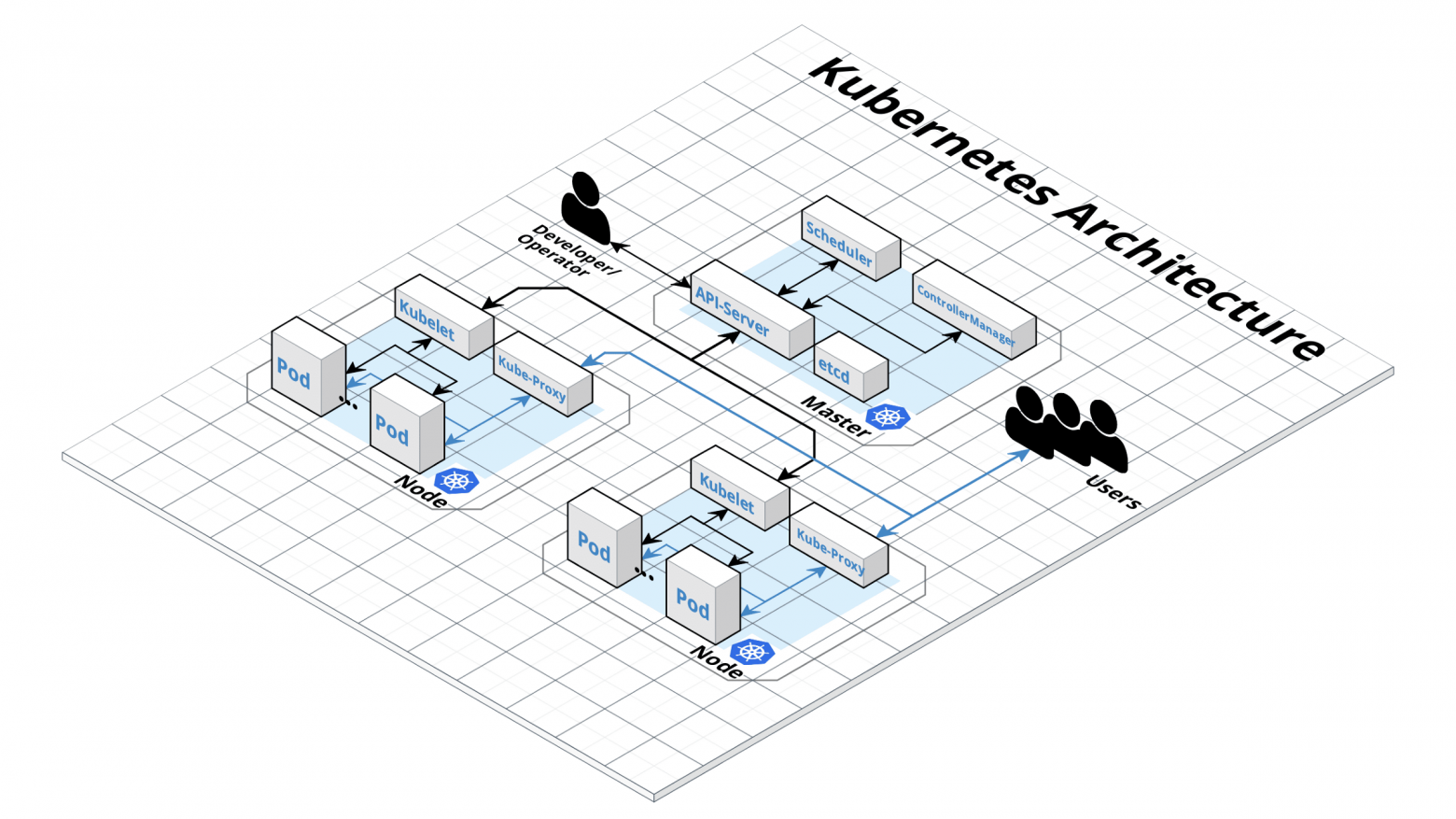
ansible-playbook --become -i inventory/$CLUSTER/hosts cluster.yml
Ansible выполняет несколько операций, и если все они успешны, кластер будет выглядеть так, как на этой картинке.
Тестирование
Чтобы протестировать кластер, войдите в мастер, переключитесь на root и в kubectl выполните команду kubectl cluster-info, чтобы получить информацию о кластере.Вы увидите подробную информацию о главной конечной точке и службах в кластере.
Если с кластером все в порядке, создайте пользователя информационной панели Kubernetes, используя следующие команды.
# Create service account
kubectl create serviceaccount cluster-admin-dashboard-sa
# Bind ClusterAdmin role to the service account
kubectl create clusterrolebinding cluster-admin-dashboard-sa \
--clusterrole=cluster-admin \
--serviceaccount=default:cluster-admin-dashboard-sa
# Parse the token
kubectl describe secret $(kubectl -n kube-system get secret | awk '/^cluster-admin-dashboard-sa-token-/{print $1}') | awk '$1=="token:"{print $2}'
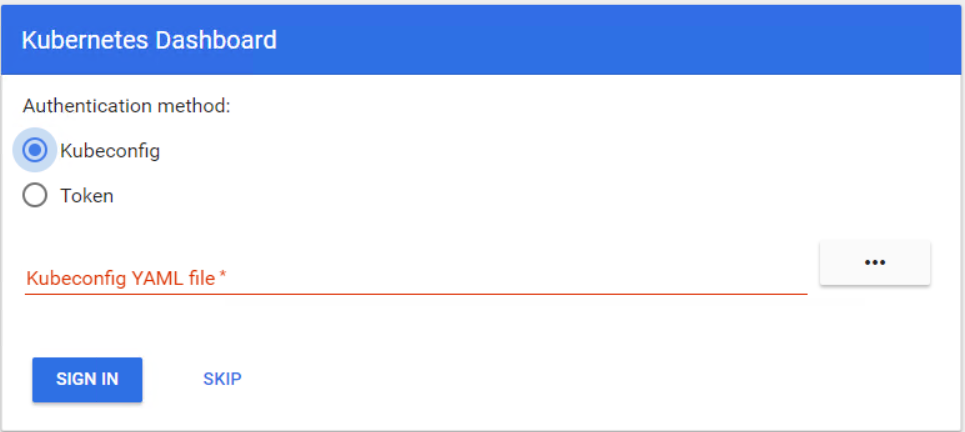
Теперь вы можете войти в свою панель управления, используя свой токен.
Во-первых, вам необходимо создать туннель к главному серверу Kubernetes, поскольку панель мониторинга по-прежнему доступна локальному хосту через порт 8001. После этого вы можете получить доступ к панели мониторинга, используя URL-адрес localhost:8001. Теперь выберите «Токен», введите токен и войдите в систему.
Вы готовы приступить к работе с кластером Kubernetes. В этой статье вы увидели, насколько легко развернуть и настроить кластер Kubernetes в облаке OpenStack.
Теги: #Системное администрирование #Администрирование серверов #Kubernetes #DevOps

-
Ноутбук Toshiba Satellite A300-20F
19 Oct, 24 -
Событие В Стиле Стартапа
19 Oct, 24 -
Карты Google Как Игровое Поле
19 Oct, 24 -
Учебное Пособие По Фотографии На Iphone
19 Oct, 24


